Retinal Diseases, Laser Procedures and Surgery
Laser Procedures
Laser Photocoagulation for Vitreo-Retinal Conditions
What is a Laser?
A laser is a strong beam of light. There are many different types of lasers and they are made when an electric current is passed through a gas or crystal. The specific substance determines the laser’s color and its use.
An ophthalmologist uses different types of lasers to perform a variety of laser procedures.
How is a Laser used in Ophthalmology?
Retina specialists use two types of laser procedures to treat the eye.
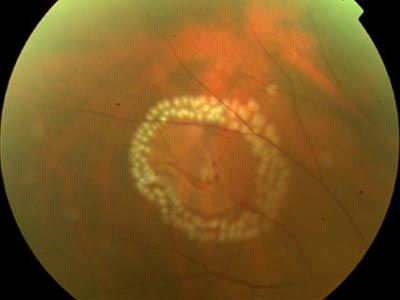 In the office retina specialists use two types of laser procedures to treat the eye, laser photocoagulation (thermal for diabetic vascular leak) and ocular photoactivation (PDT for macular degeneration).
In the office retina specialists use two types of laser procedures to treat the eye, laser photocoagulation (thermal for diabetic vascular leak) and ocular photoactivation (PDT for macular degeneration).
Laser retinopexy is often performed in conjunction with surgical treatments for retinal detachment, such as vitrectomy or pneumatic retinopexy.
Eye Problems often Treated with Laser Procedures
Retina specialists primarily treat diabetes and retinal tears or detachments with a laser.
Retinal tears or detachment. A tear in the retina can lead to a retina detachment and result in loss of vision. If diagnosed early, a retinal tear or detachment can be repaired with a laser in the clinic. The thermal laser seals the retina to the back wall of the eye again.
Diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes damages blood vessels and can cause them to leak fluid into the retina (macular edema). Diabetes can also cause new blood vessels to grow that can bleed and cause scar tissue to grow and detach the retina. A thermal laser can aid in decreasing the leakage from blood vessels and also decrease the growth of new blood vessels.
A Laser is an intense Beam of Light
Laser procedures treat retina conditions such as retinal tears, retinal detachments, diabetic macular edema, and proliferative diabetic retinopathy. A thermal laser is commonly used by retina specialists for treatment in the clinic. Laser procedures are very effective for these conditions. Like any procedure, however, there are risks of side effects and complications. Your ophthalmologist can talk with you about those.
Florida
Clermont
Daytona Beach
Fernandina Beach
Fleming Island
Kissimmee
Jacksonville Riverside
Jacksonville Southside
Lady Lake
Lake City
Lake Mary
Mount Dora
Orange City
Orlando
Palatka
Palm Coast
St. Augustine
Titusville
Wildwood
Georgia
Mondays - Fridays: 8AM to 5PM
Saturdays - Sundays: Closed
In Case of Emergency: 911
contact@floridaretinainstitute.com



